Introduction
Vitamin D is an important vitamin that helps our bodies absorb calcium and phosphorus. It also has many other benefits for our health, including reducing serious diseases.
Despite its importance, many people are deficient in vitamin D. In fact, it is estimated that 1 billion people worldwide are deficient in this vitamin. This is because we don’t get enough exposure to sunlight, which is the main source of vitamin D.
In this blog post, we will explore the health benefits of vitamin D and how you can get more of it in your diet. We will also address some of the misconceptions about this vitamin and dispel some of the myths surrounding it.
What is vitamin D?
Vitamin D is a fat- soluble vitamin that is naturally present in very few foods, added to others, and available as a dietary supplement. It is also produced endogenously when ultraviolet rays from sunlight strike the skin and trigger vitamin D synthesis. Vitamin D obtained from sun exposure, food, and supplements is biologically inert and must undergo two hydroxylations in the body for activation. The first occurs in the liver and converts vitamin D to 25- hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D], also known as calcidiol. The second occurs primarily in the kidney and forms the physiologically active 1,25- dihydroxyvitamin D [1,25(OH)2D], also known as calcitriol
What are the benefits of vitamin D?
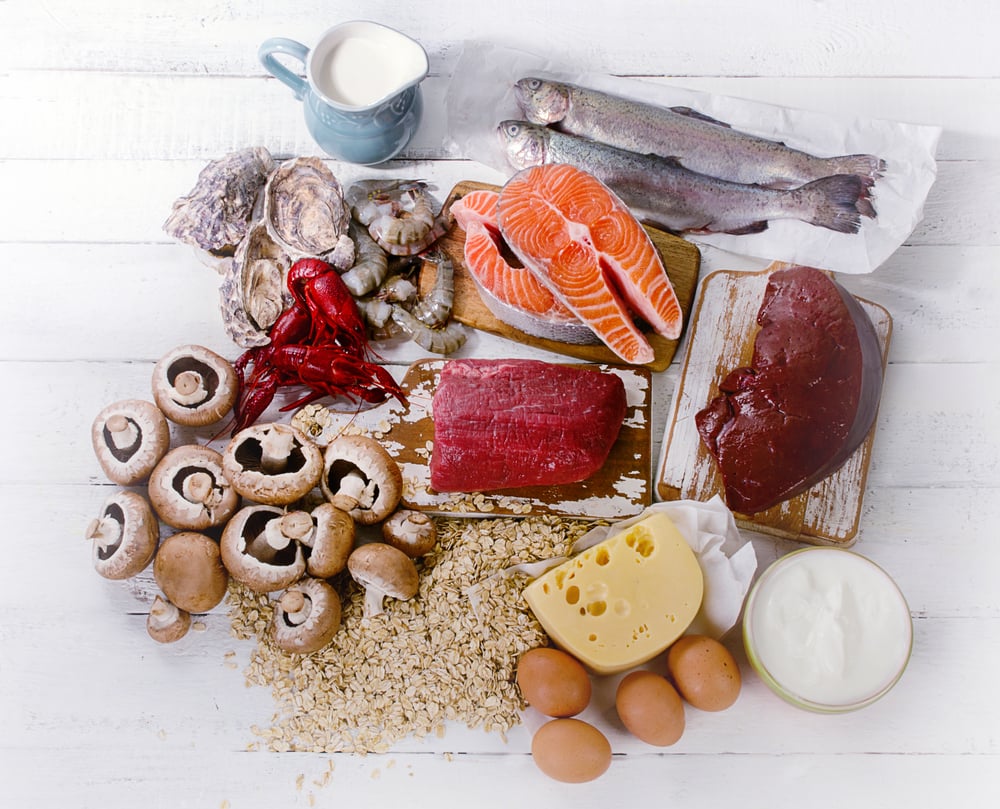
Vitamin D is an important nutrient that helps keep our bones and muscles healthy. It can be found in food sources such as fish, eggs, and dairy, and it can also be made in our bodies when our skin is exposed to sunlight. Vitamin D is important for many reasons, including improving bone health, reducing the risk of falls, and reducing the risk of some serious diseases.
To wrap things up
Vitamin D is an essential nutrient that plays a role in many aspects of health. Although you can get vitamin D from exposure to sunlight, food, and supplements, many people are still deficient in this nutrient. Vitamin D deficiency can lead to a number of health problems, including bone loss and heart disease. If you think you may be deficient in vitamin D, talk to your doctor about testing and treatment options.